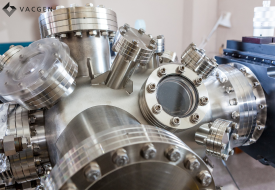
Synchrotron science shines across disciplines, illuminating a pathway for scientific discoveries. Synchrotrons use synchrotron radiation, which is produced when charged particles, typically electrons, are accelerated to nearly the speed of light in a circular or spiral path by strong magnetic fields. This process generates intense beams of light that cover a broad spectrum, from infrared to X-rays.
vacuum technology
In case you haven’t heard already, VACGEN are going green. We’ve installed 609 solar panels on our UK headquarters roof and are soon to be installing EV charging points too.
- Dec 11 2023
The Fundamentals of Photoemission Spectroscopy
Introduction
Photoemission spectroscopy is a powerful experimental technique used to study the elemental and electronic structure of materials in various states such as solids, liquids and gases. The application covers a wide range of scientific fields, with the main focus on surface chemistry and materials science. The most common forms of photoemission spectroscopy (PES) are X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Ultra-Violet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS) and Angle Resolved photoelectron spectroscopy (ARPES). Let’s explore some of the fundamental aspects of this powerful tool.
Introduction
The semiconductor industry relies heavily on vacuum technology for various processes and applications. Vacuum, in this context, refers to an environment with very low pressure and a near absence of gas molecules. Here are some key ways in which vacuum technology is used in the semiconductor industry: